In today’s cryptocurrency era, blockchain technology faces many challenges regarding scalability, transaction speed, and energy efficiency. However, with the advent of the new DAG Blockchain technology, these issues have been partially addressed. So, what is DAG Blockchain? Let’s explore this technology in detail through this article.
What is DAG Blockchain?
Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) is an advanced cryptocurrency technology with a directed graph structure that has no cycles. Unlike traditional blockchain, where transactions are grouped into blocks linked in a chain, DAG uses a complex graph made up of vertices (nodes) and edges (links) to validate transactions without the need to group them into blocks.
DAG solves several major issues faced by traditional blockchain, particularly in scalability and transaction speed. By allowing transactions to be validated and processed concurrently, DAG can handle thousands of transactions in a short time without network congestion.

How does DAG Blockchain work?
In a DAG system, each transaction is represented as a vertex in the graph, and these vertices are connected by edges. New transactions can reference and validate multiple older transactions, rather than depending on the previous transaction as in traditional blockchain. This enables faster processing of transactions and saves time.
In this way, DAG does not require mining like traditional blockchain, where miners compete to find blocks and validate transactions. This reduces energy costs and makes the network’s security more efficient.
Benefits of DAG Blockchain
Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) blockchain offers several advantages over traditional blockchain, particularly in cryptocurrency, IoT applications, and microtransactions. Here are some of the key benefits of DAG technology:
- High transaction speed: With DAG, transactions do not need to queue as they do in traditional blockchain. Instead of processing each transaction in a block, DAG allows multiple transactions to be validated simultaneously, reducing congestion and speeding up transaction processing. This is particularly useful for applications that require handling thousands of transactions per second without affecting network performance.
- Scalability: DAG has superior scalability compared to traditional blockchain. As the DAG network grows, its transaction processing capability is not limited by the number of blocks or miners. Instead, the network can handle and process multiple transactions concurrently without experiencing congestion. This makes DAG an ideal solution for applications with high transaction volumes and scalability needs.
- Energy efficiency: One of the major benefits of DAG is that it does not require complex mining mechanisms like traditional blockchain. Since there is no need for miners to compete to create new blocks, DAG significantly reduces energy consumption. This not only helps lower operational costs but is also environmentally friendly, making DAG a more sustainable and eco-friendly choice compared to blockchains that rely on Proof of Work (PoW) mining.
- Low transaction costs: In the DAG system, there is no need for blocks or miners to validate transactions, which helps reduce transaction costs. DAG networks do not require high transaction fees like traditional blockchains (such as Bitcoin or Ethereum), making them a cost-effective solution for microtransactions or applications requiring low-cost computations.
- Enhanced decentralization: DAG improves decentralization in cryptocurrency networks. Since there are no miners or central organizations managing transaction validation, anyone participating in the network can contribute to the validation process without competing to create blocks. This reduces power concentration and enhances the network’s decentralization.
- High reliability: With DAG, each transaction is validated by older transactions without waiting for a transaction to complete as in traditional blockchain. This improves reliability and ensures that transactions can be processed instantly, creating a fast and reliable system.
- High security: While DAG has not yet achieved the same level of security as traditional blockchains, its security is being improved by using consensus algorithms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake in some DAG networks. Transactions in DAG are validated by multiple sources, helping reduce the risk of attacks and enhancing network security.
- Wide applications: Due to its fast transaction processing and energy efficiency, DAG can be applied in various fields, including Internet of Things (IoT), microtransactions, financial systems, and supply chains. DAG is also particularly useful in environments that require fast and efficient transactions, such as financial payments and international money transfers.
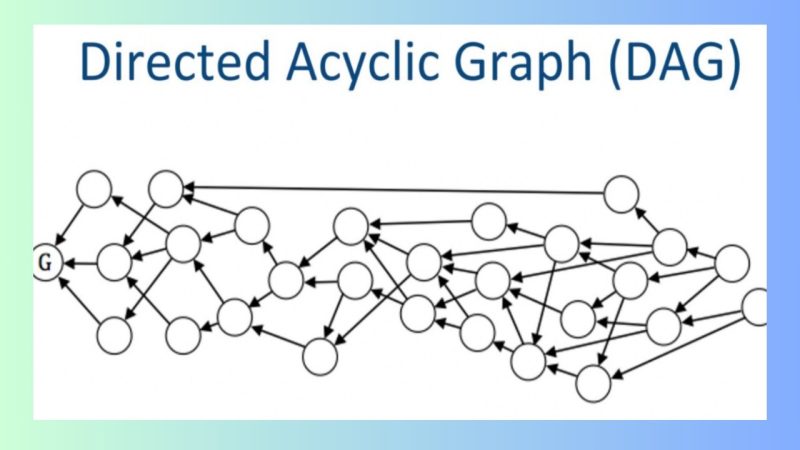
Limitations of DAG Blockchain
Despite offering significant benefits, such as fast transaction speeds, scalability, and low energy consumption, DAG technology still has some limitations that need to be addressed for widespread adoption. Here are some key limitations of DAG Blockchain:
- Not fully decentralized: One of the major issues with DAG Blockchain is that decentralization is not fully achieved. Compared to traditional blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum, DAG has not reached the same level of decentralization. While DAG eliminates the need for miners, the lack of a fully distributed consensus mechanism could lead to power concentration in the hands of a few entities or organizations controlling the network.
- Handling large transaction volumes: While DAG offers better scalability than traditional blockchain, processing large volumes of transactions in a short period remains a challenge. Some DAG systems, especially when the network becomes congested, may struggle to maintain stable and efficient transaction processing speeds. Although transactions can be validated concurrently, performance improvements are needed when the network experiences high participation.
- Security challenges: DAG uses various consensus algorithms and does not have a standardized process for transaction validation like traditional blockchains (e.g., Proof of Work or Proof of Stake). While DAG can protect the network through cross-validated transactions, in practice, when transaction volumes increase, some DAG systems may struggle to maintain security without causing issues or being vulnerable to attacks.
- Risk of 51% attacks: Like traditional blockchain, DAG can face the risk of a 51% attack. Although the DAG network does not require miners to compete to create blocks, a single organization or small group could control a majority of transactions and validations within the network. If a group controls more than 50% of transactions and validations, they could cause inconsistencies and interfere with legitimate transactions, leading to a 51% attack.
- Data integrity issues: Some DAG systems may struggle to maintain data integrity as transaction volumes increase. In some cases, validating and storing old transactions can become problematic, especially if transaction volumes are high and the network is not fully optimized. This could result in data duplication, discrepancies, or synchronization issues between nodes in the network.

Applications of DAG Blockchain
Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) is not just a theoretical technology; it is already being applied in several advanced blockchain platforms. Below, we will explore how DAG Blockchain is being utilized in major projects such as U2U Chain, Nano, IOTA, and Casper.
U2U Chain: A DAG-based Blockchain network
U2U Chain is designed to solve scalability and performance issues in traditional blockchain systems. Aiming for fast transaction processing, U2U Chain has chosen DAG Blockchain technology to optimize its network and ensure scalability without sacrificing security or decentralization.
Application of DAG in U2U Chain
U2U Chain uses DAG to replace blocks in traditional blockchain, reducing transaction fees and optimizing processing times. Each transaction on U2U Chain is validated concurrently, ensuring quicker and more efficient transactions.
Furthermore, DAG technology helps U2U Chain save significant energy compared to traditional blockchains like Bitcoin, where mining requires large amounts of power. U2U Chain is building Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePIN), especially in IoT and GPU Computing sectors, using DAG to scale its network and increase transaction processing capacity.
Nano: Fee-free cryptocurrency
Nano is a cryptocurrency operating on a DAG Blockchain system aimed at creating a fast, efficient, and fee-free payment network. Nano uses a variant of DAG called block lattice to replace traditional blockchain.
Application of DAG in Nano
Each user in Nano has a separate block chain called a block lattice, and transactions occur when the sender and receiver make changes to their own chains. This system allows Nano to achieve instant transactions without the need for miner validation or intermediaries.
With DAG, Nano can handle a high volume of transactions without being affected by block creation like traditional blockchains. Nano’s major advantage is fee-free transactions and fast confirmation times, making it ideal for microtransactions and direct payments.

IOTA: A Blockchain without blocks
IOTA is a pioneering project in DAG Blockchain technology, being one of the first networks to not use blocks for transaction storage. IOTA uses a technology called Tangle, a DAG-based system that allows transactions to be validated without the need for block mining.
Application of DAG in IOTA
In IOTA, users are not only recipients of transactions but also have the responsibility to confirm two previous transactions, helping to create a decentralized network without the need for miners. Each new transaction must validate at least two older transactions, thereby creating a Tangle structure without the need for blocks.
IOTA is particularly useful for Internet of Things (IoT) applications, where a large number of devices communicate with each other, requiring quick transaction processing with no transaction fees. This model helps IOTA save energy and reduce costs compared to traditional blockchains, increasing the network’s scalability.
Casper: DAG-Based Blockchain for enterprises
Casper is a blockchain developed specifically for businesses, and it uses DAG as part of its Highway consensus algorithm. This project focuses on improving data transmission capabilities between validators and minimizing the time required to validate transactions.
Application of DAG in Casper
Casper uses DAG to improve the speed and efficiency of the data aggregation process between validators in the network. This model makes data transmission more efficient, reduces latency, and enhances scalability for large enterprise applications.
DAG in Casper also supports fast transaction validation and processing without compromising security, allowing businesses to deploy applications that require high integrity. Thanks to DAG, Casper can efficiently process transactions while maintaining high levels of decentralization and security.
So, with this article, you have the answer to the question “What is DAG Blockchain?” DAG Blockchain is a groundbreaking technology in the cryptocurrency industry, promising to solve problems faced by traditional blockchains such as scalability, transaction speed, and energy consumption. Although there are still some challenges related to security and decentralization, DAG has great potential to change how cryptocurrency networks operate in the future.
With increasingly developed and improved applications, DAG could become an indispensable part of the future of the cryptocurrency industry, especially in areas requiring fast and efficient transactions such as Internet of Things (IoT) and microtransactions.
Hopefully through this article, Modern Techera has helped you better understand the term “What is DAG Blockchain?” If you have any questions about this term, please leave a comment below so we can help you answer in detail!